1. Summary
HTML5 is a markup language that is used to structure and deliver material on the internet. The World Wide Web Consortium has proposed it as the fifth and last major HTML version (W3C). The HTML Living Standard is the current specification. The Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group (WHATWG), a collaboration of key browser vendors, maintains it (Apple, Google, Mozilla, and Microsoft).
HTML5 was first released in a public-facing form on 22 January 2008, with a major update and “W3C Recommendation” status in October 2014. HTML5 introduces markup and application programming interfaces (APIs) for complex online applications, as well as detailed processing models to encourage more compatible implementations. It also extends, enhances, and rationalises the markup accessible for documents. HTML5 is a candidate for cross-platform mobile applications for the same reasons, as it has capabilities intended with low-power devices in mind.
a. What is HTML?
HTML is a markup language that determines the structure of web pages at their most basic level. HTML informs browsers how to process content and show it to the viewer using tags and attributes. You can indicate which parts of the document are a title, a list, an image, and so on using HTML. You can also hyperlink a word, embed a picture, change the font’s italics, and do a lot more.
HTML was first published in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee and is today utilised by 92 per cent of all websites, including most of the ones you visit. “HTML” is the abbreviation for “Hypertext Markup Language.” Let’s take a closer look at each word to see what HTML actually implies.
Hypertext, often known as hyperlinks, is the text that contains references to other text or pages. With a click of the mouse, you can go anywhere on the internet. We can use hyperlinks to navigate to another section of the same page, a different page on the current website, or an entirely different website, rather than reading a web page in the linear order that the author put out, as we would in print. A PDF, email, or multimedia item, such as a video or audio file, can all be opened via hyperlinks.
b. Is HTML a programming language?
HTML’s status as a programming language is a point of contention among web developers and specialists. Although others argue that the two aren’t mutually incompatible, the majority of people consider HTML to be a markup language rather than a programming language.
To comprehend this distinction, we must first grasp what a programming language is. All programming languages must “do” something, whether it’s evaluating expressions, declaring variables, or altering data. These languages tell computers not just what to do but also how to accomplish it. In web development, JavaScript is the most extensively utilised programming language. Python, Java, and C/C++. are some of the other popular programming languages.
HTML, is a language that doesn’t actually “do” anything. It merely provides the content that browsers need to show. HTML is unconcerned about how the content is presented in the browser as long as it is displayed. To put it another way, HTML serves a structural rather than a functional purpose.
c. What is HTML used for?
HTML is a programming language that is mostly used to create web pages. HTML is free to use and assures that your text, graphics, and other elements are shown as intended because it is open-source and supported by all modern browsers. All web pages would simply text files if they didn’t contain HTML:
Not only can you use HTML to format texts with headers, paragraphs, lists, and other elements, but you can also use hyperlinks to embed photos, videos, audio files, and other multimedia. You can also connect to other web pages on the same or different websites. Visitors will be able to simply navigate your website and bounce between web pages hosted on different web servers as a result of this.
You’d still have a very basic and clear web page after adding headings, graphics, and hyperlinks — and that’s by design. HTML is designed to provide a simple foundation for adding Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and JavaScript (JS). You may change the colour, font, and alignment of items with CSS to modify your styling and layouts. You may use and JS to add dynamic functionality like pop-ups and photo sliders to your website.
HTML can also be used to make items other than web pages. It can be used to create tables for data organisation. Forms can be used to collect information from users, handle transactions, make bookings, or place orders. HTML can also be used to create emails.
d. How to Write HTML?
HTML is simply plain text tagged with markup, as previously stated. This markup, in further detail, is made up of tags and attributes. Here’s a diagram to help you visualise the syntax.
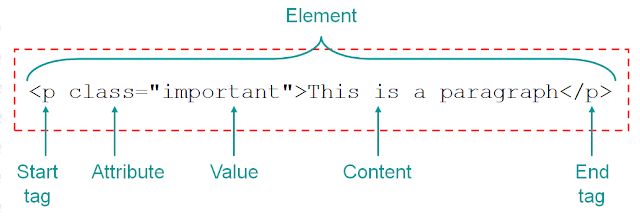
Source: hubspot.com
HTML Tags
Tags are used to identify HTML elements[Ma1] . An opening and closing tag can be found on almost every element. The element name is enclosed by the brackets “<” and “>” in the opening tags, which come before the text. Closing tags are identical to opening tags, except that the element name is preceded by a reverse slash.
Let’s say you want to add a paragraph to your website with the content “This is a paragraph.” You’ll use the HTML paragraph tags to wrap it: <p></p>.
These three items are all that is required to create an HTML paragraph element. The most frequent HTML elements are an opening tag, a closing tag, and the content in between. The opening tag of some HTML elements, such as br> (break), is called an empty tag.
The names of the elements are case-insensitive. They can be written in capital letters, lowercase letters, or a combination of the two. The <p> tag, for example, can also be written as <P>. However, it is recommended that the name be written in lowercase at all times.
HTML Attributes
While tags are required for all HTML elements, attributes are only required for a subset of them. An attribute gives additional information about an HTML element, which can be either mandatory or optional.
An image element, for example, must always include a source property with the image URL or file path as its value. Otherwise, the browser will be unable to determine which image to render. The anchor element, which is used to build hyperlinks, must also have a href property with a value that indicates the destination of the link. If a visitor clicks on the anchor element otherwise, the browser will not take them anywhere.
Other characteristics aren’t required, but they’re a good idea to include. A browser can, for example, display an image without the alt attribute, which contains image alt text. However, without an alternative language description, a reader with visual impairments may struggle to understand what the image is trying to represent.
Many elements have their own set of properties that influence how the material is displayed on the page. Inside the beginning tag, attributes can be written in any sequence. You can’t have more than one instance of the same attribute in the same HTML tag, though.
e. Steps to add footer tags to your webpage using HTML5
HTML5’s new HTML element tags promise to make the life of website developers a little more structured and easier. The new header and HTML5 footer elements are significantly more ordered and cleaner than the old division tags. Not that division tags are obsolete, but the new tags offer a more efficient approach to organise your content on the page. Enroll in the HTML5 tutorials now to learn about HTML5 and how to apply the new capabilities in your web pages.
To utilise the footer tag, go through the instructions below:
f. Create an HTML5 document
To make a website with HTML, you must first create an HTML file. This file will be posted to your web server and will contain all of the HTML for your web page. When a visitor searches for your website, the server will send an HTML file to the visitor’s browser, which will render the page as desired.
The DOCTYPE element must be used at the top of the page to create an HTML5 document. The structure of an HTML5 page is as follows:
g. Add Footer Tags to the Sections
HTML5 adds a number of new tags to the mix. For example, the article tag produces a segment that browsers identify as an article. The header tag adds a section to the page’s header.
The footer tag can be used in any portion of the page or many sections of the page. Let’s start by creating an article section, then adding a footer tag to include the article’s details, such as author, date, and sources.
Take a look at the code in the next section.
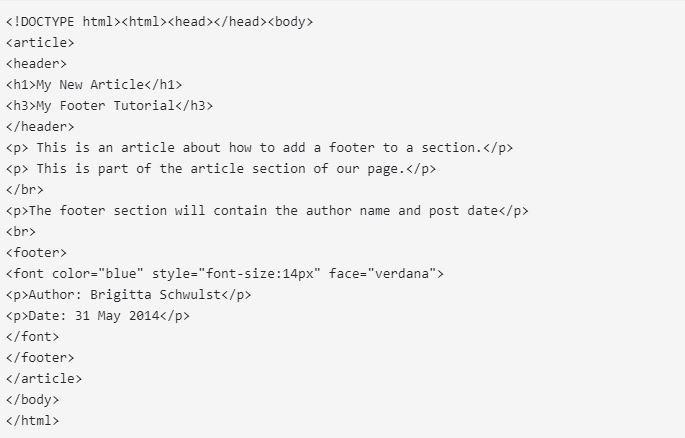
Source: udemy.com
Using the article tag, the code creates an article section. Then, for our article heading, we added a header section to our article section. The article’s body comes next, followed by a footer tag that includes information about the author and publishing date.
The article, header, and footer tags make it easier for search engine bots to index your content. Although there is no evidence that search engines have included the new tags in their search and SEO algorithms, experts appear to agree that pages formatted using the new HTML5 elements will be indexed better in the future. It’s vital to remember that not all browsers support HTML5, so alternative solutions for browsers that don’t support HTML5 are necessary.
h. Add the footer tag to the page itself.
Users that explore the web frequently come across a page and have no idea what website it was published on or what the website’s goal is. Page footers are a wonderful location to put information about the page or links to certain sections of your website that aren’t always visible in the main navigation system.
The <footer> tag can be used to create a footer section for your website. You are free to include as many footer components as you want on your page. Take a look at the code below:
i. Conclusion
HTML5 introduces markup and application programming interfaces (APIs) for complex online applications, as well as detailed processing models to encourage more compatible implementations. It also extends, enhances, and rationalises the markup accessible for documents. HTML5 is a candidate for cross-platform mobile applications for the same reasons, as it has capabilities intended with low-power devices in mind.
click here for more articles

